| Fabric name | Bamboo fabric |
| Fabric also known as | Bamboo rayon, bamboo viscose, bamboo linen |
| Fabric composition | Semi-synthetic viscose cellulose extracted from bamboo or yarn made from bamboo fibers |
| Fabric possible thread count variations | 250-500 |
| Fabric breathability | High |
| Moisture-wicking abilities | High |
| Heat retention abilities | Medium |
| Stretchability (give) | High |
| Prone to pilling/bubbling | High |
| Country where fabric was first produced | China |
| Biggest exporting/producing country today | China |
| Recommended washing temperatures | Warm |
| Commonly used in | Clothing and household textiles |
Bamboo fabric is becoming an essential material in sustainable fashion.
Known for its eco-friendly properties, it is now widely used in apparel manufacturing.
This blog will delve into its characteristics, production process, costs, and environmental impact.
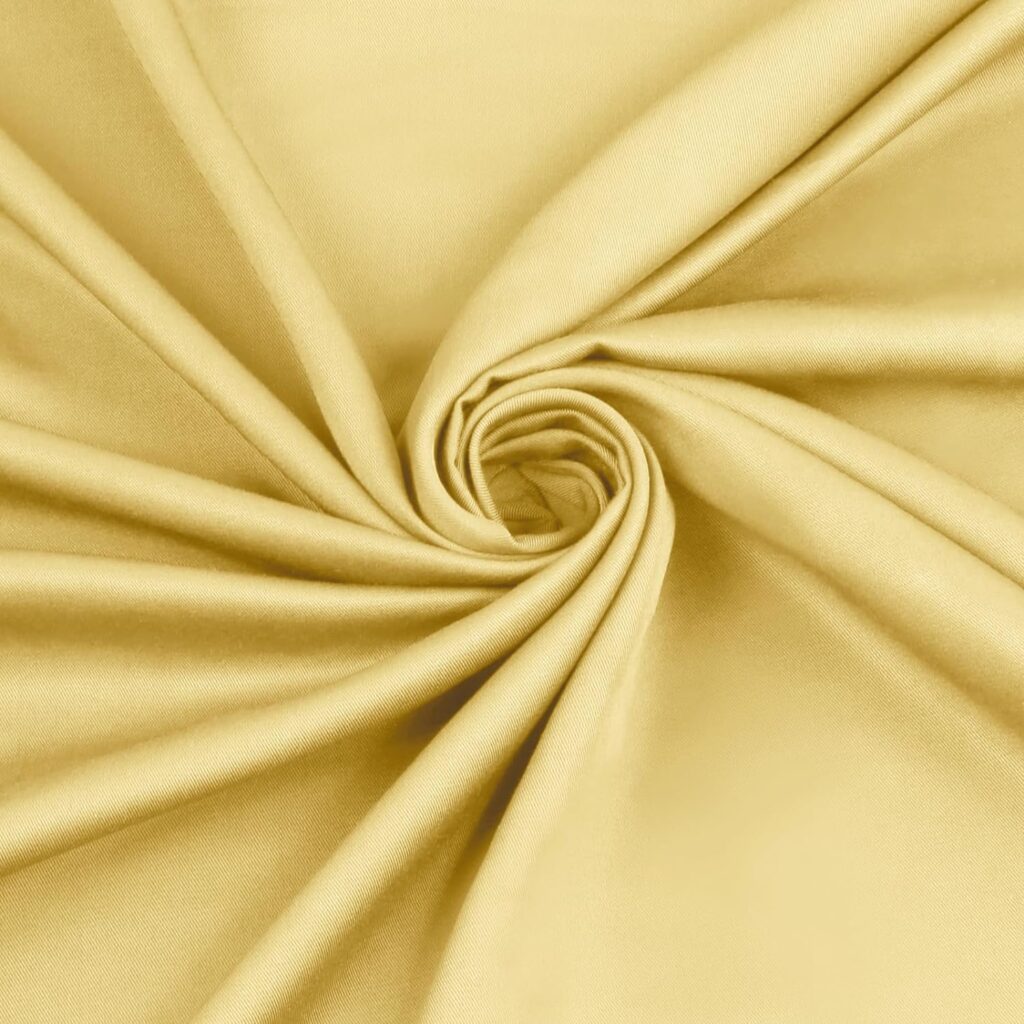

What is Bamboo Fabric?
Bamboo fabric is made from bamboo plant fibers, available in two main types: bamboo viscose, produced chemically for softness, and bamboo linen, mechanically processed for eco-friendliness. It’s praised for being breathable, soft, and moisture-wicking, making it ideal for apparel and home textiles.
Origin and Source of Bamboo Fibers
Bamboo grows rapidly, mainly in China, needing little water or pesticides. Viscose uses chemicals to turn bamboo into a silky fabric, while linen is more sustainable but coarser.

Historical Significance and Modern Usage
Bamboo fabric has gained popularity recently due to eco-consciousness. Its versatility spans from apparel to home textiles.
Bamboo Fabric Today
Bamboo viscose is common due to its softness, though sustainability concerns are driving innovation in closed-loop systems. Bamboo linen offers a more eco-friendly option, though less common due to production costs.
At Modaknits, we focus on creating sustainable bamboo-based garments, combining comfort with environmental responsibility.
What Makes Bamboo Fabric Unique?
Bamboo fabric is known for several outstanding qualities:
- Softness: Bamboo viscose feels exceptionally smooth and luxurious, comparable to silk, making it ideal for clothing worn close to the skin.
- Breathability: It allows for excellent air circulation, keeping the wearer cool and comfortable, particularly in warm climates.
- Antibacterial Properties: Bamboo fabric retains some of the plant’s natural antibacterial qualities, helping garments stay fresh longer.
- Eco-friendliness: Bamboo grows rapidly without needing much water or pesticides, making it a more sustainable textile choice.
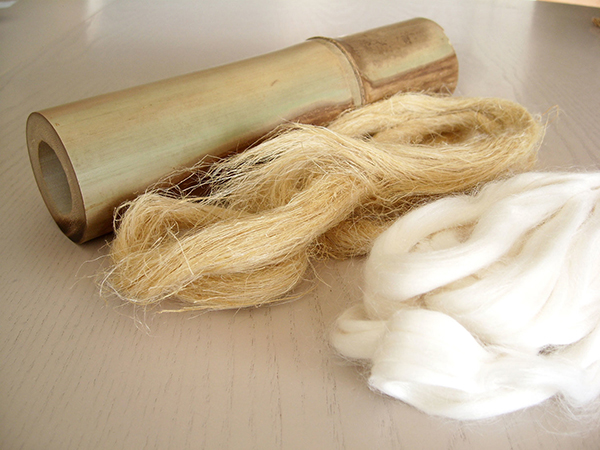

Comparison with Other Fabrics
- Bamboo vs. Cotton: While both are breathable, bamboo is softer and more moisture-wicking, though cotton is more durable.
- Bamboo vs. Polyester: Bamboo is more eco-friendly and breathable, whereas polyester traps heat but dries faster.
- Bamboo vs. Linen: Bamboo is smoother and more flexible, while linen is rougher and wrinkles easily.
Bamboo fabric’s unique blend of softness, breathability, and sustainability makes it an excellent choice for various apparel applications.
How is Bamboo Fabric Made?
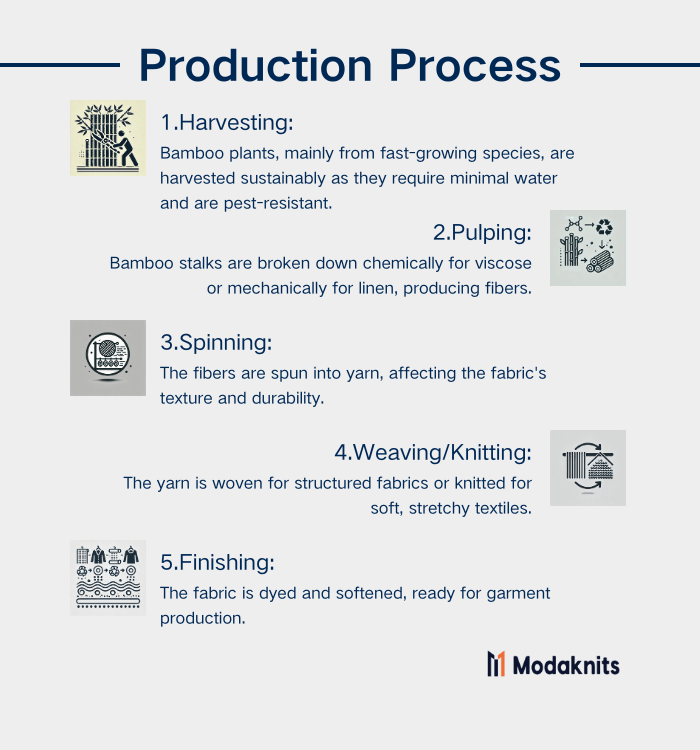
Production Process
- Harvesting: Bamboo fabric begins with the harvesting of bamboo plants, primarily from fast-growing species. These plants are naturally pest-resistant and require little water, making them a sustainable resource.
- Pulping: In the chemical process for bamboo viscose, bamboo stalks are broken down using solvents to create a pulp, which is then processed into fibers. The mechanical process, used for bamboo linen, involves crushing the stalks and using enzymes to extract the fibers.
- Spinning: The bamboo fibers are spun into yarn, which influences the texture and strength of the fabric.
- Weaving/Knitting: Bamboo yarn is either woven for structured textiles or knitted for softer, stretchier fabrics.
- Finishing: The final bamboo fabric undergoes treatments such as dyeing or softening, preparing it for use in garments.
Regions Known for Bamboo Production
- China: The largest producer of bamboo, known for efficient manufacturing of bamboo textiles.
These processes ensure the creation of both luxurious bamboo viscose and eco-friendly bamboo linen for a wide variety of textile uses.
What Are the Types of Bamboo Fabric?
- Bamboo Viscose:
This is the most common form, made through a chemical process that dissolves bamboo into a pulp before spinning it into fibers. Bamboo viscose is valued for its silky, luxurious feel and is often used in apparel like T-shirts, dresses, and sleepwear. Its softness and breathability make it highly popular. - Bamboo Linen:
Made through mechanical processing, bamboo linen is more eco-friendly but has a rougher texture. It’s commonly used for sustainable fashion products like shirts and pants that require durability. - Blended Bamboo Fabrics:
Bamboo fibers are sometimes blended with cotton, polyester, or other fibers to enhance the durability, stretch, or texture of the final fabric. Blended bamboo fabrics combine the benefits of bamboo with the strength of other fibers, making them versatile for various clothing applications like activewear and casual apparel.
Each type brings its own unique qualities, making bamboo fabric a flexible and environmentally conscious choice for different fashion needs.
How is Bamboo Fabric Used in Textiles?

- Casual and Everyday Wear:
Bamboo fabric is known for its soft and breathable texture, making it an excellent choice for T-shirts, casual dresses, and loungewear. Its natural ability to wick moisture away from the skin ensures comfort throughout the day, even in warmer climates. - Activewear:
Thanks to its moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, bamboo fabric is ideal for sportswear such as leggings, T-shirts, and sports bras. These qualities help athletes stay dry and comfortable while preventing odors during workouts. - Undergarments and Socks:
Bamboo’s hypoallergenic and antimicrobial nature makes it perfect for sensitive skin. It’s commonly used in socks, underwear, and intimate apparel where comfort and hygiene are paramount. - Luxury Loungewear and Sleepwear:
Bamboo’s smooth, silky texture has made it a popular material in high-end loungewear and sleepwear. Its breathability and moisture management offer a luxurious feel, while its eco-friendly nature aligns with sustainable fashion trends. - Home Textiles:
Beyond clothing, bamboo is used for home textiles like bed linens and towels. Its moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties provide both comfort and hygiene, making bamboo fabric a preferred choice for bedding.
Bamboo fabric’s versatility in apparel manufacturing highlights its potential to deliver eco-friendly, comfortable, and high-performance garments across various categories.
How Much Does Bamboo Fabric Cost?
The cost of bamboo fabric can vary based on production methods, quality, and region. Here’s an overview of typical price ranges:
Bamboo Fabric Costs in the United States
- Bamboo Viscose: Generally priced between $5 to $10 per meter. This is the most affordable option due to its chemical processing.
- Bamboo Linen: Typically ranges from $12 to $20 per meter. The eco-friendly mechanical process makes it pricier.
Bamboo Fabric Costs in China
- Bamboo Viscose: Prices usually range from $4 to $8 per meter due to lower production costs.
- Bamboo Linen: More affordable compared to Western markets, with prices around $10 to $15 per meter.

Factors Influencing Bamboo Fabric Prices
- Production Method: Bamboo viscose is cheaper due to the chemical process, while bamboo linen is pricier because of its mechanical production.
- Freight and Shipping Costs: One of the reasons for price differences between the U.S. and China is the shipping and import duties associated with transporting the fabric. Freight costs from China can significantly impact the final price, making bamboo fabric more affordable locally compared to Western markets.
At Modaknits, we provide high-quality bamboo fabrics at competitive prices, taking into account both local and global sourcing to ensure a balance between affordability and sustainability for our clients.
How Does Bamboo Fabric Impact the Environment?
Bamboo fabric’s environmental impact largely depends on its production process. Bamboo itself is a highly sustainable resource, as it grows rapidly, requires little water, and does not need pesticides. However, the production of bamboo viscose involves chemical processes that can harm the environment if not managed responsibly. Conversely, bamboo linen, which is mechanically processed, is much more eco-friendly, but it’s less common due to higher production costs.
Water Usage
Unlike cotton, bamboo requires minimal irrigation, reducing water consumption in its cultivation. This makes bamboo farming more sustainable, especially in areas where water scarcity is a concern.
Chemical Use in Viscose Production
The production of bamboo viscose can involve harsh chemicals like sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide. These chemicals, if not managed in a closed-loop system, can contaminate water sources and negatively affect both the environment and factory workers.
Pesticide-Free Cultivation
Bamboo grows without the need for pesticides or synthetic fertilizers, reducing soil and water contamination compared to conventional farming methods for crops like cotton.

Energy Consumption and Emissions
The production of bamboo fabric, especially in the viscose process, requires energy, though advancements in energy-efficient technology can help mitigate the impact. Mechanical bamboo fabric production, as seen with bamboo linen, uses fewer chemicals and less energy, making it a greener option.
Biodegradability and Waste
Bamboo fabric is biodegradable, meaning it breaks down naturally, unlike synthetic fabrics. However, chemical treatments used in viscose production may affect its biodegradability. Mechanically processed bamboo fabrics, such as bamboo linen, remain more eco-friendly in this regard.
Sustainability Efforts
Some manufacturers are adopting closed-loop systems for bamboo viscose production to recycle chemicals and minimize waste. Certifications like OEKO-TEX and GOTS ensure that bamboo fabric is produced sustainably, with minimal environmental impact.
At Modaknits, we prioritize sourcing bamboo fabrics from suppliers who employ environmentally responsible production methods.
We aim to balance performance, comfort, and sustainability in every fabric we manufacture.
Ensuring Bamboo Fabric Quality and Certification
At Modaknits, we focus on selecting high-quality bamboo fabrics to create eco-friendly garments.
As a manufacturer, it’s essential for us to work with fabrics that meet strict environmental and quality standards.
Key Quality Indicators:
- Fiber Softness: Bamboo viscose offers silk-like softness, while bamboo linen is textured and durable.
- Breathability: Bamboo fabrics are naturally breathable and moisture-wicking, making them perfect for apparel.

Certifications and Sustainability:
- GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard): Ensures the fabric is produced under eco-friendly and ethical practices.
- OEKO-TEX® Standard 100: Certifies that bamboo fabric is free from harmful chemicals, ensuring safety for skin contact.
By sourcing bamboo fabrics with these certifications, Modaknits ensures the production of high-quality, sustainable clothing for our clients.nmentally conscious, aligning with global standards for responsible fashion.
For more information about our fabrics or to explore our product catalog, please contact us.













