| Fabric name | Charmeuse |
| Fabric also known as | Crepe-backed satin |
| Fabric composition | Silk or synthetic fibers |
| Commonly used in | pants, lingerie, negligees, slips, tank tops, dresses, robes, handkerchiefs, ties |
| Fabric breathability | High |
| Moisture-wicking abilities | Medium |
| Heat retention abilities | Low |
| Stretchability (give) | Low |
| Prone to pilling/bubbling | Low |
| Fabric possible thread count variations | 12 to 30 momme |
| Country where fabric was first produced | China |
| Biggest exporting/producing country today | China |
| Recommended washing temperatures | Dry clean or cold |

What is Cashmere Fabric?
Cashmere fabric is a luxurious textile known for its exceptional softness, warmth, and lightweight properties. Derived from the fine undercoat fibers of cashmere goats, which are primarily found in regions such as Mongolia, China, Nepal, and Kashmir, cashmere is significantly finer, stronger, and lighter than sheep’s wool. This exquisite fabric has been valued for centuries and is synonymous with luxury and comfort in various cultures.
Origin and Source of Cashmere Wool
The production of cashmere wool begins with the cashmere goats, specifically their undercoat, which provides the finest and softest fibers. These goats are well-suited to the harsh climates of the Gobi Desert and Central Asia, where they develop a dense undercoat to protect them from the cold. The fibers are collected during the molting season in spring when the goats naturally shed their winter coats.
Historical Significance and Luxury Status
The history of cashmere fabric dates back to the 3rd century BC, with evidence suggesting its production began much earlier. Cashmere wool was first traded with Turkestan and then made its way to the Middle East. From there, it was introduced to Europe, where it quickly became a prized material. By the 19th century, cashmere production had become a significant industry in Europe, particularly in France, which favored this luxurious material for its softness and warmth.
Today, China is the largest producer of cashmere, with a thriving cottage industry still present in Central Asian nations. Despite the rise of synthetic fibers, there remains no true synthetic equivalent to the unique properties of cashmere, ensuring its continued demand and luxury status.

Cashmere Fabric Today
Modern production of cashmere continues to be concentrated in China, which leads the global market. However, traditional goat herders in Mongolia and the Kashmir region still contribute to the cashmere industry. As global awareness of ethical and sustainable production practices increases, there is a growing emphasis on producing cashmere in ways that minimize environmental impact and ensure animal welfare.
The enduring appeal of cashmere lies in its unmatched softness and warmth. High-quality cashmere garments are a testament to this fabric’s luxurious nature, making them highly sought after in the fashion industry.
At Modaknits, we harness these qualities to produce premium cashmere apparel, combining traditional craftsmanship with modern techniques to meet the diverse needs of our clients.
What Makes Cashmere Fabric Unique?
Cashmere fabric is highly prized for its luxurious qualities and exceptional performance characteristics. Sourced from the soft undercoat of cashmere goats, this fabric stands out in the textile industry for its unique combination of softness, warmth, and lightweight properties, making it a preferred choice for high-end fashion and accessories.
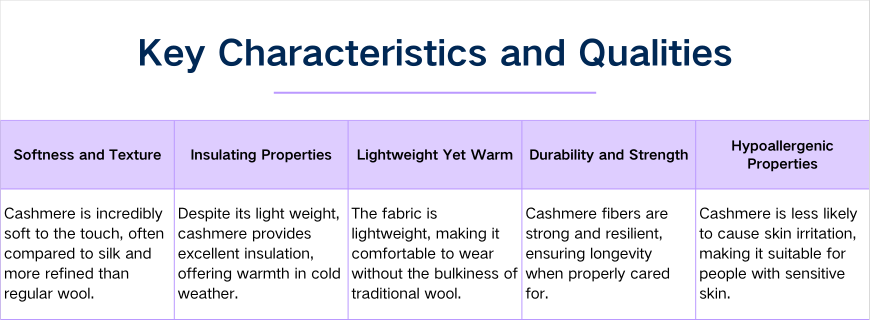
1.Softness and Texture: Cashmere is renowned for its incredible softness, often described as feeling like a blend of silk and fine wool, making it highly desirable for luxury garments.
2.Insulating Properties: Despite being lightweight, cashmere offers excellent insulation, providing warmth in cold weather without the bulk.
3.Lightweight Yet Warm: Cashmere garments are light and comfortable, offering warmth without the heaviness of traditional wool.
4.Durability and Strength: Cashmere fibers are strong and durable, ensuring longevity when properly cared for, making it a lasting investment.
5.Hypoallergenic Properties: Cashmere is less likely to cause skin irritation, making it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies to coarser wools.
Comparison with Other Fabrics
Cashmere vs. Wool: While both cashmere and wool come from animal fibers, cashmere is significantly softer, lighter, and warmer than regular sheep’s wool. The finer fibers of cashmere give it a luxurious feel, whereas wool can be coarser and heavier. Additionally, cashmere’s superior insulation properties make it a more effective fabric for cold weather, though it comes at a higher cost due to its rarity and the labor-intensive process of harvesting cashmere fibers.
Cashmere vs. Synthetic Fibers (like Polyester): Compared to synthetic fibers such as polyester, cashmere offers far superior comfort, breathability, and natural insulation. Polyester, while durable and cost-effective, cannot match the luxurious feel or the thermal properties of cashmere. Cashmere naturally regulates temperature and provides warmth, whereas polyester tends to retain heat and can feel less breathable. Moreover, cashmere’s biodegradability gives it an environmental edge over synthetic fibers, which are derived from petrochemicals and contribute to plastic pollution.
How is Cashmere Fabric Made?
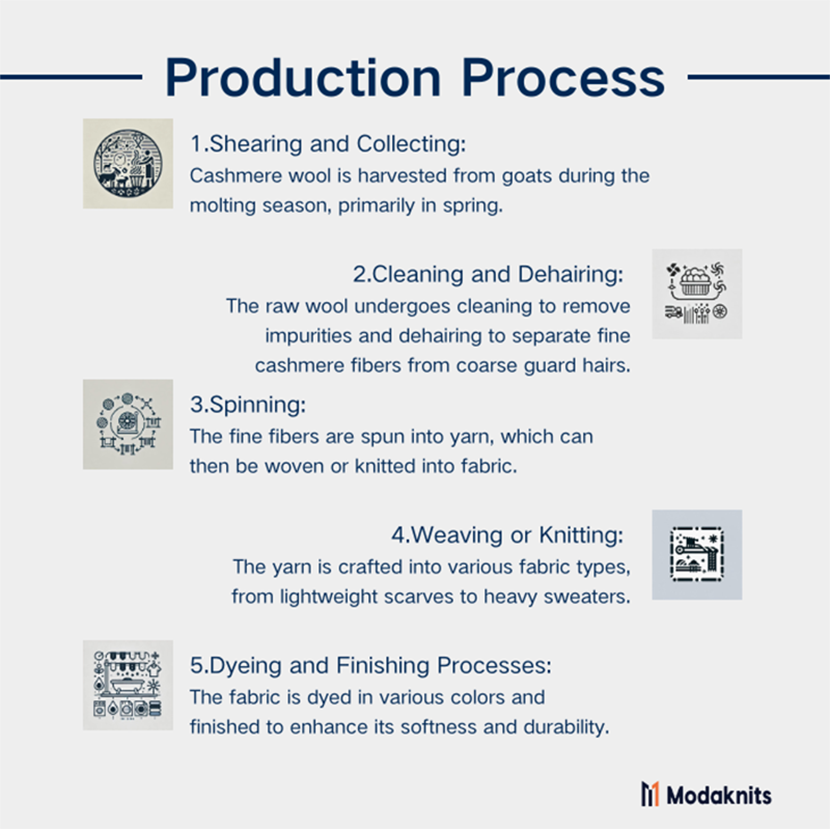
The production of cashmere fabric involves several meticulous steps that ensure the highest quality of this luxurious material. Each stage, from shearing to finishing, is carefully managed to preserve the unique properties of cashmere.
- Shearing and Collecting Cashmere Wool: Harvested in spring, cashmere wool is collected by combing or shearing goats, gathering soft undercoat fibers.
- Cleaning and Dehairing the Fibers: Raw wool is cleaned to remove impurities and dehaired to separate fine cashmere from coarse guard hairs.
- Spinning the Fibers into Yarn: Fine cashmere fibers are spun into yarn, aligning and twisting them into continuous threads for weaving or knitting.
- Weaving or Knitting the Yarn into Fabric: Yarn is woven or knitted into fabric, creating various types from lightweight scarves to heavy sweaters.
- Dyeing and Finishing Processes: Fabric is dyed carefully to maintain softness and undergoes finishing processes to enhance durability and softness.
Regions Known for Cashmere Production
- Mongolia: Mongolia is one of the largest producers of high-quality cashmere. The harsh climate conditions contribute to the development of long, fine fibers that are highly sought after. Mongolian cashmere is known for its warmth and softness.
- China: China is the world’s largest producer of cashmere, particularly in regions like Inner Mongolia. Chinese cashmere is renowned for its fine texture and is often considered some of the best in the world. The country’s advanced processing techniques ensure high-quality output.
- Nepal: Nepalese cashmere is known for its craftsmanship and traditional methods. Artisans in Nepal often produce hand-spun and hand-woven cashmere products, which are highly valued for their quality and uniqueness.
- Kashmir: The region of Kashmir lends its name to cashmere and has a long history of producing this luxurious fabric. Kashmiri cashmere is famous for its delicate feel and fine quality, often used in high-end shawls and scarves.
These regions not only contribute to the global supply of cashmere but also bring unique characteristics to the fabric based on their specific local breeds and environmental conditions. Each region’s approach to cashmere production reflects a rich heritage and commitment to quality.
What are the Types of Cashmere Fabric?
Cashmere fabric comes in various forms, each with unique characteristics and applications. Here’s an overview of the main types:
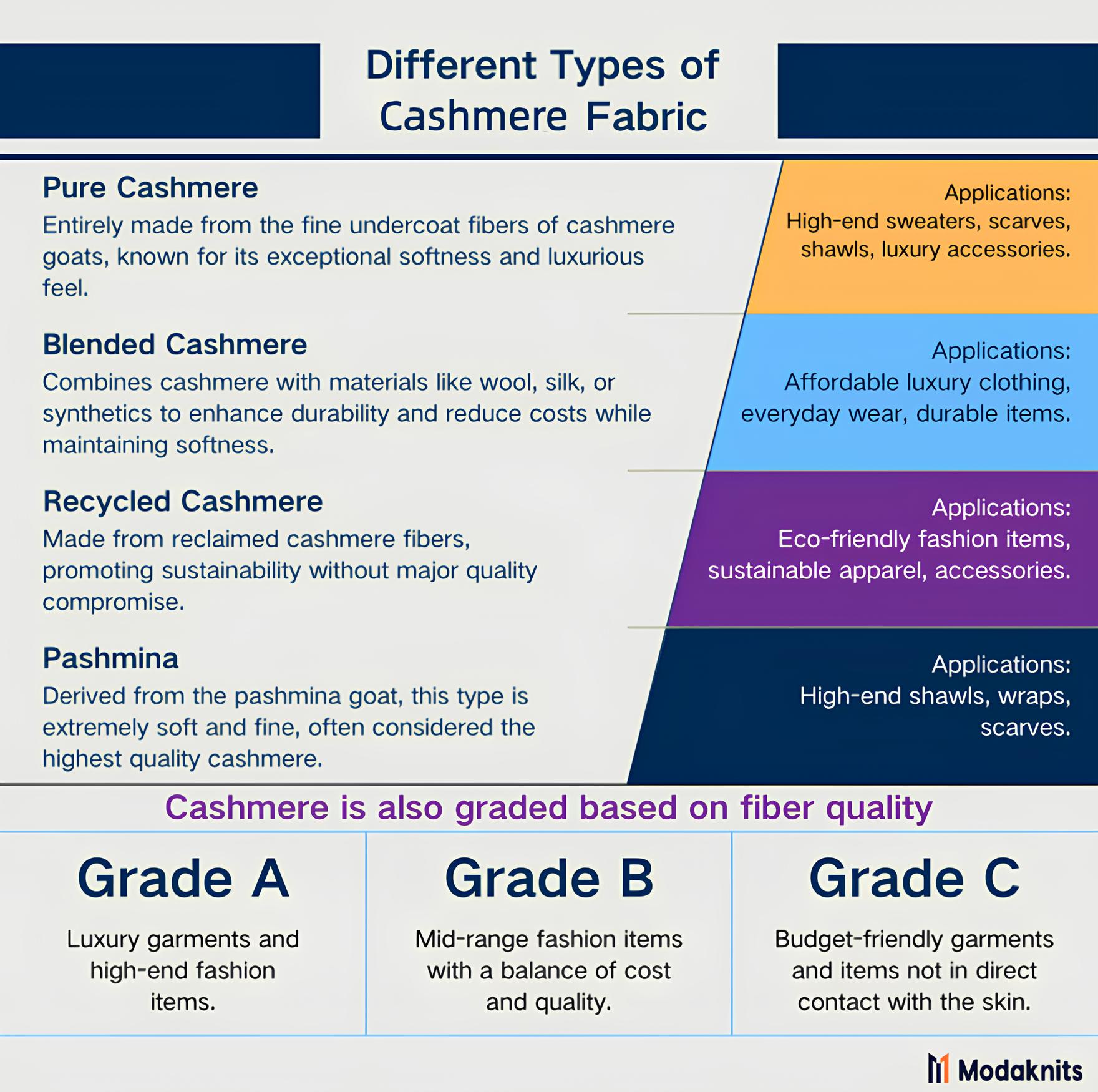
1. Pure Cashmere
Pure cashmere is made entirely from the fine undercoat fibers of cashmere goats. It is renowned for its exceptional softness, warmth, and luxurious feel.
Applications: High-end sweaters, scarves, shawls, and luxury accessories.
2. Blended Cashmere
Blended cashmere combines cashmere fibers with other materials like wool, silk, or synthetic fibers. This blend aims to enhance durability, reduce costs, and maintain a degree of softness.
Applications: Affordable luxury clothing, everyday wear, and items requiring additional durability.
3. Recycled Cashmere
Recycled cashmere is made from reclaimed cashmere fibers, often sourced from used garments. This sustainable option promotes environmental responsibility without compromising too much on the quality.
Applications: Eco-friendly fashion items, sustainable apparel, and accessories.
4. Pashmina
Pashmina is closely related to cashmere, derived from the pashmina goat. It is extremely soft and fine, often considered the highest quality form of cashmere wool.
Applications: High-end shawls, wraps, and scarves.
5. Grade A, B, and C Cashmere
Cashmere is also graded based on fiber quality. Grade A cashmere is the finest and softest, while Grade B and C are progressively coarser and less expensive.
Applications:
- Grade A: Luxury garments and high-end fashion items.
- Grade B: Mid-range fashion items with a balance of cost and quality.
- Grade C: Budget-friendly garments and items not in direct contact with the skin.
These variations allow cashmere to cater to a wide range of market needs, from high-end luxury to eco-friendly and budget-conscious products.
How is Cashmere Fabric Used?
Cashmere fabric is celebrated for its luxurious feel and exceptional qualities, making it a versatile material used across various applications. From high-end fashion garments to home textiles and even industrial uses, cashmere’s unique properties ensure it remains a top choice for consumers seeking both comfort and elegance. At Modaknits, we leverage our extensive experience and state-of-the-art technology to produce premium cashmere apparel, meeting the diverse needs of today’s discerning clients.

Apparel Applications
Cashmere is a staple in the fashion industry, used extensively in a variety of clothing items. Its unparalleled softness and warmth make it a preferred material for high-end garments. Common apparel applications include:
- Sweaters and Cardigans: Known for their luxurious feel and warmth, making them popular in both everyday and luxury wear.
- Scarves and Shawls: Offering lightweight warmth and a soft touch, ideal for both casual and formal settings.
- Suits and Jackets: Providing a touch of sophistication and comfort in professional and formal attire.
- Hats and Gloves: Ensuring warmth and style during colder months.
Home Textiles
Cashmere’s luxurious qualities extend beyond clothing, making it a favored choice for home textiles. Its use in home decor brings a touch of elegance and comfort. Key applications include:
- Blankets and Throws: Offering unparalleled warmth and softness, perfect for cozying up during the colder seasons.
- Pillow Covers: Adding a luxurious feel to any living space, enhancing comfort and aesthetic appeal.
- Cushions and Upholstery: Used in high-end furniture to provide a soft, comfortable surface that is also visually appealing.
Industrial and Other Uses
While primarily known for its use in fashion and home textiles, cashmere also finds applications in various other sectors. Its fine quality and durability make it suitable for:
- High-End Upholstery: Used in luxury vehicles and high-end furniture, providing both aesthetic appeal and comfort.
- Interior Design Elements: Incorporating cashmere in decor items to enhance the luxury and comfort of living spaces.
Cashmere fabric’s versatility and superior qualities make it a prized material in multiple sectors. Whether in everyday apparel, luxurious home textiles, or high-end industrial applications, cashmere continues to be a symbol of elegance and quality.
How Does Cashmere Fabric Impact the Environment?
Cashmere fabric has a notable environmental impact throughout its lifecycle, from production to disposal. Understanding these impacts is crucial for promoting sustainable practices in cashmere production.
Environmental Concerns
- Overgrazing and Desertification:
- Impact: Cashmere goats require significant grazing areas. Overgrazing by large herds can lead to soil erosion and desertification, particularly in regions like Mongolia and China, where much of the world’s cashmere is produced.
- Result: This environmental degradation can destroy ecosystems, reduce biodiversity, and contribute to climate change by disrupting the natural carbon cycle.
- Resource Intensive:
- Impact: Producing cashmere is resource-intensive. Each goat produces a relatively small amount of cashmere, requiring large herds to meet global demand.
- Result: This high resource requirement increases pressure on land and water resources, exacerbating environmental stress in cashmere-producing regions.
- Ethical and Social Considerations:
- Impact: Ethical considerations in cashmere production include the humane treatment of animals and fair labor practices. In some regions, workers may face poor working conditions and low wages.
- Result: Ensuring ethical practices can mitigate social harm and improve the welfare of both workers and animals.

Innovations in Sustainable Cashmere Production
- Recycled Cashmere:
- Description: Recycled cashmere is made from reclaimed fibers, often sourced from used garments. This approach reduces the need for new raw materials and minimizes waste.
- Benefit: Promotes sustainability by extending the life cycle of cashmere fibers and reducing the environmental footprint of cashmere production.
- Eco-Friendly Farming Techniques:
- Description: Sustainable farming practices include rotational grazing, which helps prevent overgrazing and maintains soil health.
- Benefit: These methods can reduce environmental impact and promote the long-term sustainability of cashmere farming.
- Certifications for Sustainable Production:
- Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS): Ensures organic and environmentally friendly production processes.
- Fair Trade: Guarantees ethical treatment of workers and animals, promoting fair wages and humane practices.
- Benefit: Certifications provide consumers with confidence in the sustainability and ethical standards of their cashmere products, encouraging more responsible consumption.
Modaknits’ Commitment to Sustainability
We are dedicated to implementing and promoting sustainable practices in our cashmere apparel manufacturing. We collaborate with ethical suppliers and utilize eco-friendly production methods to reduce our environmental impact. Our commitment to sustainability includes supporting humane animal treatment, fair labor practices, and the use of recycled cashmere.
By prioritizing these values, we aim to produce high-quality cashmere garments that meet both the demands of our customers and the needs of our planet. In conclusion, while cashmere fabric has significant environmental impacts, innovations in sustainable production and responsible practices can mitigate these effects.
At Modaknits, we are committed to leading the way in sustainable cashmere manufacturing, inviting brands to collaborate with us in creating luxurious, eco-friendly apparel.
What Should You Look for When Buying Cashmere Fabric?
When purchasing cashmere fabric, it’s essential to understand key quality indicators and verify authenticity through recognized certifications. Here’s a detailed guide on what to look for:
Quality Indicators
- Fineness and Length of Fibers: High-quality cashmere is characterized by its fine and long fibers. These qualities contribute to the fabric’s softness and durability. Typically, the finer and longer the fibers, the softer and more luxurious the cashmere will feel.
- Softness and Feel: Authentic cashmere should feel exceptionally soft and smooth to the touch. This luxurious feel is one of the main reasons why cashmere is highly prized in the textile industry.
- Purity and Blend Ratios: Pure cashmere is often preferred for its superior quality, but blends with other fibers can offer different benefits. Check the label for the percentage of cashmere; a higher percentage indicates better quality. Blends should still feel soft and luxurious, even if they include other materials like silk or wool to enhance durability and reduce costs.

Certifications and Authenticity
- Certifications and Labels: To ensure the quality and authenticity of cashmere products, look for recognized certifications. These can include:
- The Cashmere and Camel Hair Manufacturers Institute (CCMI): This certification ensures the fiber content is genuine and meets the standards for high-quality cashmere.
- Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS): This certification ensures the fabric is produced using organic and environmentally friendly processes.
- Good Cashmere Standard (GCS): Developed by the Aid by Trade Foundation, this standard focuses on animal welfare, social criteria, and environmental protection in cashmere production.
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100: This label guarantees that the fabric has been tested and is free from harmful substances.
By paying attention to these indicators and seeking out certified products, you can ensure that you are purchasing high-quality cashmere fabric that meets your expectations for luxury and sustainability.
Why Choose Modaknits for Cashmere Fabric Apparel Manufacturing?
At Modaknits, we pride ourselves on our extensive experience in crafting high-quality cashmere apparel. Utilizing cutting-edge technology and sustainable practices, we ensure that every piece we produce meets the highest standards of excellence.
Commitment to Quality, Sustainability, and Customer Satisfaction
- Premium Materials: We source the finest cashmere fibers to create garments that are luxurious and long-lasting.
- Meticulous Manufacturing: Our rigorous manufacturing processes ensure exceptional quality and durability in every product.
- Eco-Friendly Practices: Our commitment to sustainability means we use environmentally responsible methods, aligning with the increasing demand for eco-friendly fashion.
We invite brands to partner with Modaknits for producing top-tier cashmere apparel.
For more information or to request our product catalog, please contact us.
Let’s create something extraordinary together.













